What is Access Control List (ACL)?
Access control list (ACL) is a set of rules that define the permissions granted to users or system processes for accessing specific resources, such as files, directories, or network devices. Each entry in an ACL specifies a subject (user or process) and the level of access allowed (e.g., view, edit, print). ACLs are used to enforce security policies by ensuring that only authorized users can perform certain actions on sensitive data and systems. By clearly delineating access rights, ACLs help protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and ensure compliance with security regulations.
How ACLs Work
Each resource (e.g., file, folder, or network route) has its own ACL, which includes entries specifying:
- Who (users or groups) can access the resource
- What actions they’re allowed to take
For example:
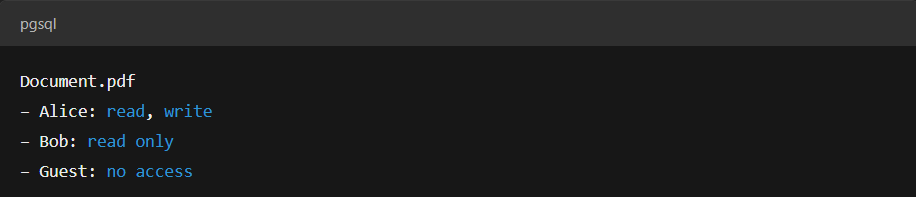
The system checks this list whenever someone attempts to access the file. If the user is listed with the required permission, access is granted; otherwise, it’s denied.
Types of Access Control Lists
- File System ACLs
File system ACLs control access to files and directories on an operating system. They specify which users or groups can perform actions like read, edit, or share a file. - Network ACLs
Network ACLs are used to control incoming and outgoing traffic at the network layer. They are typically configured on routers, firewalls, or cloud infrastructure to filter packets based on rules. - Directory Service ACLs
These are ACLs applied within identity and directory services like Active Directory or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), used to control access to organizational resources like users, groups, printers, and devices. - Application-level ACLs
Application-level ACLs define access to components or data within a software application. They allow developers or admins to restrict actions based on user roles or identities. - Cloud-Based ACLs
Modern cloud platforms use ACLs to define permissions on cloud storage resources and APIs.
ACL vs. RBAC vs. ABAC
Model | Control Based On | Flexibility | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
ACL | Individual user or group permissions | High granularity | Files, directories, networks |
RBAC | User roles | Easier to manage at scale | Enterprise systems |
ABAC | User, resource, and environmental attributes | Very dynamic | Cloud and zero trust environments |
How Fasoo Enhances ACLs with Persistent Protection
Fasoo Enterprise DRM (FED) goes beyond ACLs by applying file-level access controls that remain active no matter where the file goes. This ensures:
- Access policies follow the document, even when downloaded, shared externally, or moved to the cloud.
- Permissions can be changed in real time, even after distribution
- Granular access controls (e.g., view-only, block print, block screen capture, apply dynamic watermark) are enforced on any device
- Full audit trail of file access and usage is provided
ACLs define access at the point of origin. Fasoo enforces access wherever the data lives.
Resources

Product Overview

Video

Use Case
Fasoo Enterprise DRM
Meet with a DataSecurity Specialist

Brochure
Learn more about
Fasoo Enterprise DRM

